In the perpetual inventory method, goods are recorded as a B/S (Balance Sheet) account called "Merchandise" when purchased, and each time goods are shipped, the Merchandise account is reduced to synchronize the inventory with the accounting balance of the Merchandise account. In contrast, in the periodic inventory method (three-way method), purchases are recorded as an expense in a P/L (Profit and Loss) account, and at the end of the month, the purchases, beginning inventory, and ending inventory valuation are transferred to the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS). Accounting System in Indonesia The cloudification of accounting systems is advancing in Indonesia, with the three major local cloud systemsAccurate, Zahir, and Jurnalleading the market. However, in reality, it is said that fewer than 8% of domestic companies have implemented accounting systems. This is why new cloud-based accounting systems continue to be launched in what might seem like an already saturated Indonesian market. It suggests that both domestic and international IT startups see significant potential for cloud accounting systems to expand their market share locally. In Indonesia, automated journal entries due to the widespread use of accounting systems have become commonplace, and over the ... 続きを見る

Flow of Accounting Journal Entries Generated by Business Systems
Within business systems, the flow from procurement management to general accounting is as follows:
In the Case of an ERP System
Depending on the business system, some perform journal generation and posting to the ledger simultaneously after receipt processing, based on invoice-based debt registration rather than purchase registration.
In the Case of an Accounting System
In the Case of an Accounting System Ledger (G/L)
Perpetual Inventory Method
In an integrated system for sales, procurement, inventory management, and accounting, when sales are recorded on an accrual basis (shipment basis), the products are simultaneously transferred to COGS (Cost of Goods Sold) and expensed. This allows for continuous tracking of the accounting inventory balance. A/R (Accounts Receivable) against sales is temporarily recorded in an unrealized account (A/R Accrued) until the invoice is issued, at which point A/R Accrued is reclassified to A/R. This is known as the perpetual inventory method.
Since the perpetual method requires knowing the cost (unit price) of goods at every shipment, the inventory valuation and the G/L (General Ledger) inventory account balance are synchronized in real-time. The valuation of inventory receipts and issues is either calculated using the moving average unit price or the First-In, First-Out (FIFO) method with full lot management.
In this case, the COGS account and Inventories account in the accounting system's G/L are updated in real-time.
- (Dr) Inventories 500,000 (Cr) A/P Accrued 500,000
- (Dr) A/P Accrued 500,000 (Cr) A/P 500,000
For shipment-based sales recognition on an accrual basis, the entries are as follows:
- (Dr) A/R Accrued 600,000 (Cr) Sales 600,000
- (Dr) A/R 600,000 (Cr) A/R Accrued 600,000
- (Dr) COGS 500,000 (Cr) Inventories 500,000
For inspection-based sales recognition, where the invoice is issued and sales are recorded after customer inspection, the entries are as follows:
- (Dr) Shipment Clearing 600,000 (Cr) Inventories 600,000
- (Dr) COGS 500,000 (Cr) Shipment Clearing 500,000
- (Dr) A/R 600,000 (Cr) Sales 600,000
Periodic Inventory Method (Three-Way Method)
In the periodic method, goods received during the month are expensed to the Purchase account. At the end of the month, through closing journal entries, the Opening Stock, Purchases, and Closing Stock are consolidated into the COGS account. The difference between "beginning inventory + purchases - ending inventory" is recorded as COGS under the periodic inventory system.
- (Dr) Purchase 500,000 (Cr) A/P Accrued 500,000
- (Dr) A/P Accrued 500,000 (Cr) A/P 500,000
- (Dr) A/R Accrued 600,000 (Cr) Sales 600,000
- (Dr) A/R 600,000 (Cr) A/R Accrued 600,000
In the inventory management system, quantities are increased or decreased with each receipt or issue, and unit prices for purchased goods can be updated using the moving average method. However, the received inventory is accumulated as an expense in the Purchase account, and the B/S inventory value in the accounting system remains unchanged until the end of the month.
For factory management, essential information includes current inventory quantities and payment schedules for receivables and payables. Since finalizing the P/L and B/S at month-end is sufficient, the G/L inventory balance is not updated during the month. Instead, the valuation is calculated based on a physical inventory at month-end, and the beginning and ending inventories are transferred via P/L accounts (Opening Stock and Closing Stock), synchronizing the inventory between inventory management and accounting.
Expenses Accumulated in Cost of Goods Sold
In addition to inventory receipts and issues, the following three items are transferred to COGS via closing journal entries using journal vouchers:
- Freight In (CIF Costs = Procurement Expenses) → Added to Direct Material
- Direct Labor Cost
- FOH (Factory Overhead)
By transferring CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) expenses related to procurement—such as customs duties (Bea Masuk), PPh22, PPN, and customs clearance permits (SPPB) included in the import declaration (PIB)—to the COGS account, the final COGS is determined, and Gross Profit is calculated.
Closing Journal Entries
Fixed Asset Depreciation Entries
Before transferring P/L accounts to Net Income, Depreciation expenses must be interfaced in advance from the fixed asset management system to the Fixed Asset account-specific depreciation entries.
- (Dr) Depreciation (SGA) 3 (Cr) Accumulated Depreciation (Negative Asset) 3
Note: SGA stands for Selling and General Administrative Expenses.
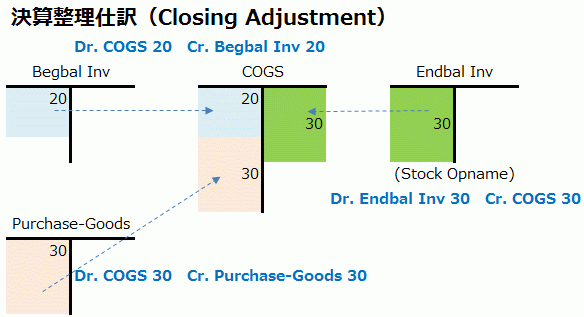
Transferring Inventory to Opening and Ending Balances
For inventory (materials, work-in-progress, finished goods), synchronization with accounting is achieved by transferring the beginning balance and ending physical inventory valuation. The Opening Stock (beginning inventory) and Closing Stock (ending inventory) accounts are contra accounts to the P/L accounts.
- (Dr) Opening Stock 20 (Cr) Inventories 20
- (Dr) Inventories 30 (Cr) Closing Stock 30
Transferring Purchase Account to Cost of Goods Sold
The Purchase account, which is also an expense account, is transferred to the COGS account, and the COGS balance becomes the cost of goods sold for the month.
- (Dr) COGS 20 (Cr) Opening Stock 20
- (Dr) COGS 30 (Cr) Purchase Goods 30
- (Dr) Closing Stock 30 (Cr) COGS 30
Reclassification of All P/L Accounts
All P/L accounts, including COGS, are fully reclassified to the Net Income (Income Summary) account.
In Indonesia, the term "Trial Balance" often refers to a general ledger balance, but Japanese accountants may request a combined trial balance.
- Summary Trial Balance: Displays the total amounts for each account in debit and credit columns.
- Balance Trial Balance: The typical T/B in Indonesia (balance only, with one side at zero).
- Combined Trial Balance: Displays both 1 and 2 in separate columns.
The worksheet consists of "T/B debit/credit columns + B/S debit/credit columns + P/L debit/credit columns" and is prepared through the closing process that separates B/S and P/L items from the T/B. However, this is generally not prepared in Indonesia.
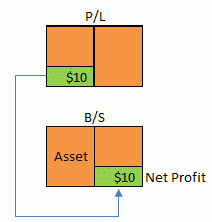
Transferring Net Income to Retained Earnings
The Retained Earnings account does not necessarily appear every month-end; it often appears only at the fiscal year-end when profit distribution occurs. In such cases, Net Profit is shown as the difference between Expenses and Income on the monthly P/L, and it is also recorded as Net Profit under the assets section of the B/S.
The Biggest Difference Between the Periodic Method and Perpetual Method
In other words, whether determining COGS by deducting the ending inventory (based on physical inventory results) at month-end or continuously updating COGS at the time of shipment, the presentation of COGS on the P/L is expressed as follows:
In system accounting, when calculating material costs, manufacturing costs, and COGS in that order, instead of consolidating the beginning inventory, monthly receipts, and ending inventory into the COGS or Purchase accounts, the G/L data is directly collected, added, and subtracted, and the result is simply pasted into the P/L in this format.
The inventory remaining at the end of the month is derived from the Closing Stock in the inventory transfer entries made in the Closing Journal, meaning it represents the portion that remains in inventory and is not expensed.
- (Dr) Opening Stock (Cr) Merchandise
- (Dr) Merchandise (Cr) Closing Stock
In the periodic method, goods received are processed in the Purchase account, so the Merchandise account only appears during inventory transfers at month-end. In contrast, the perpetual method continuously tracks inventory amounts through movements in the Merchandise account, without using accounts like Purchase, Opening Stock, or Closing Stock.
Instead, the key difference lies in how the issuance of goods is recorded compared to the periodic method.
In systems that continuously record the movement of goods, even though COGS is not calculated using the periodic method, the COGS calculation section on the P/L is written in a periodic-method style, which is likely the source of confusion.
Special Loss Treatment in the Periodic Method
Month-End Closing Process
- (Dr) Opening Stock 100 (Cr) Merchandise 100
- (Dr) Merchandise 120 (Cr) Closing Stock 120
The COGS calculation section on the P/L is currently written as follows:
Recording Special Loss for Defective Goods and Deducting from Purchases
In the periodic method, since COGS is calculated based on movements in the Purchase account, the deduction is made from the Purchase account, and the Merchandise account is only used during inventory transfers in the closing entries.
- (Dr) Special Loss 5 (Cr) Purchase 5
A common misunderstanding is: "In practice, defective goods worth 5 are removed from the ending inventory of 120 and discarded, so shouldn’t we deduct 5 from the ending 120 in the formula above? Wait, doesn’t that mean it gets included in COGS and then double-counted as a special loss later?"
Physically, defective goods are "taken out of the ending inventory in the defective goods warehouse and discarded," but since the defective portion was already expensed in the monthly Purchase account at the time of purchase, you need to either "deduct the non-expensed portion from Purchase (treat it as if it wasn’t purchased)" or "deduct it from COGS."
Deducting from the Purchase account is not necessarily wrong, but since this treats it as if it wasn’t purchased, it becomes unclear how much was actually purchased that month.
By the way, whether the special loss is recorded before or after the closing process, the impact on COGS in the P/L remains the same.
Recording Special Loss for Defective Goods and Deducting from COGS
The COGS calculation section on the P/L clearly indicates that it is deducted from COGS via another account transfer.
- (Dr) Special Loss 5 (Cr) Product Other Account Transfer 5
The result is the same, but by indirectly deducting from COGS, the original monthly purchase amount can still be identified on the P/L.
Special Loss Treatment in the Perpetual Method
Month-End Closing Process
In the perpetual method, while goods movements are continuously recorded, the beginning inventory happens to be 100, purchases and issues occur repeatedly during the month, and the ending inventory becomes 120 as a result.
Recording Special Loss for Defective Goods and Deducting from Merchandise
- (Dr) Special Loss 5 (Cr) Merchandise 5
On the P/L, this expresses that the ending inventory became 120 as a result of an additional goods issuance due to the special loss.
To reiterate, the ending inventory represents the portion not expensed and deducted from COGS. Misinterpreting this in practical terms and deducting goods from the ending inventory can lead to double-counting of expenses.
In this case, too, it becomes unclear how much was originally purchased that month.
Recording Special Loss for Defective Goods and Deducting from COGS
The COGS calculation section on the P/L clearly indicates that it is deducted from COGS via another account transfer.
- (Dr) Special Loss 5 (Cr) Product Other Account Transfer 5
Issuance Records Based on Disposal, Inventory Adjustments, Prototypes, and Internal Consumption
Cost transfers based on issuance records in the production management system include transfers within manufacturing costs or from COGS to selling and administrative expenses.
The cost of defective materials or work-in-progress is deducted from manufacturing costs. Since this is a transfer within manufacturing costs, the total manufacturing cost remains unchanged even without this entry.
- (Dr) Defective Cost (Cr) WIP Other Account Transfer
The disposal loss of finished goods after determining manufacturing costs is deducted from COGS. Without this entry, COGS would be overstated, and gross profit understated (operating profit remains the same).
- (Dr) Product Disposal Loss (Cr) Product Other Account Transfer
Prototypes are treated as selling expenses and deducted from COGS. Without this entry, COGS would be overstated, and gross profit understated (operating profit remains the same).
- (Dr) Selling & Administrative Expenses (Cr) Product Other Account Transfer
For employee meals, general administrative expenses are deducted from COGS. Without this entry, COGS would be overstated, and gross profit understated (operating profit remains the same).
- (Dr) General Administrative Expenses (Cr) Product Other Account Transfer
For jigs, they are capitalized as assets. Without this entry, COGS would be overstated, and gross profit understated (operating profit remains the same).
- (Dr) Assets (Cr) Product Other Account Transfer
Handling Differences Between System Inventory and Physical Inventory Counts
If the policy is to determine the monthly manufacturing cost as "Beginning WIP + Monthly Manufacturing Expenses - Ending WIP," there is no need to generate cost transfer entries in accounting based on issuance records from the month-end physical inventory.
This is because "Ending WIP" is an amount based on the physical inventory count, so any differences are automatically included in the monthly manufacturing cost, which is a result of the periodic method.
In this case, the manufacturing cost difference would inflate manufacturing costs, overstate COGS, and understate gross profit (operating profit remains the same).
When recording inventory differences as inventory shrinkage loss (selling & administrative expenses), it is deducted from COGS. By adding the shrinkage amount to the ending product valuation via another account transfer, the shrinkage is indirectly deducted from COGS.
- (Dr) Inventory Shrinkage Loss (Cr) Product Other Account Transfer
When transferring material differences to factory overhead within manufacturing costs, the following entry is generated, but the total manufacturing cost remains unchanged.
- (Dr) Factory Overhead (Cr) WIP Other Account Transfer
Procurement-related expenses, such as those from import declarations (PIB) or goods release approvals (SPPB), are allocated to manufacturing costs. Without this entry, manufacturing costs would be understated, COGS understated, and gross profit overstated (operating profit remains the same).
- (Dr) PIB (Cr) A/P
- (Dr) Manufacturing Cost (Cr) PIB
Entries for Inventory Revaluation Based on the Lower of Cost or Market Method
These are profit/loss entries generated when inventory is valued at the lower of the total average unit price calculated by the cost management system or the market price considering market conditions.
In cases of significant obsolescence, it is recorded as an inventory valuation loss (selling & administrative expenses). For reasons beyond normal expectations (e.g., theft or fire), it is recorded as a special loss (non-operating expense). Without this entry, for materials or WIP, manufacturing costs would be overstated (operating profit remains the same), and for finished goods, COGS would be overstated (ordinary profit remains the same).
- (Dr) Inventory Valuation Loss (Cr) WIP Other Account Transfer
- (Dr) Special Loss (Cr) Product Other Account Transfer
The market price, considering market conditions, is set in the valuation unit price master. If it is lower than the total average unit price, the difference is recorded as a valuation loss, and the valuation unit price is applied to the ending inventory valuation. If it is higher, the total average unit price is applied to the ending inventory valuation (valuation loss is 0 in this case).
- Set the market price considering market conditions in the month-end valuation unit price master.
- Calculate the valuation loss as the difference between the market price and the theoretical month-end valuation unit price from cost calculation.
- By turning on the truncation flag in the valuation type master and copying the calculation result, the beginning inventory for the next month reflects the valuation loss as an expense and carries over with a reduced valuation.
Inventory Valuation in Perpetual Method and Periodic Method
In the periodic method, purchases are unconditionally recorded in the Purchase account (expense account) upon receipt, and at month-end, the beginning and ending inventories are transferred to their respective contra accounts (Opening Stock and Closing Stock). These, along with the Purchase account, are then transferred to the COGS account to calculate the cost of goods sold. However, in Indonesia, it seems common to record purchases in an asset account (materials or merchandise) upon receipt and transfer only the consumed (sold) portion to manufacturing costs (or COGS) based on standard costs at month-end.
- Characteristics of Inventory Receipts and Issues Generating Accounting Entries (Perpetual Method)
- Need to maintain inventory valuation at all times ⇒ FIFO or moving average method is acceptable, but total average method is not.
- Real-time entry is a prerequisite; reversing the order of receipts and issues prevents accurate valuation.
- With each receipt and issue, inventory, manufacturing costs, and COGS are correctly calculated, and the P/L is automatically generated.
- Characteristics of Inventory Receipts and Issues Not Generating Accounting Entries (Periodic Method)
- Calculate COGS using the periodic method.
- Synchronize accounting with inventory using Opening Stock and Closing Stock accounts (P/L contra accounts).
- Transfer Opening Stock, Closing Stock, and Purchase accounts to the COGS account to calculate COGS.
- Transfer all P/L account balances to the Net Income account to calculate gross profit.
- Total average method is applicable.
- Since valuation is determined at month-end, negative inventory quantities during the month are not an issue.
- Inventory valuation is possible during the month using the Month-To-Date (MTD) total average unit price, but the month-end total average unit price is applied in accounting.
- Calculate COGS using the periodic method.
- Common Characteristics of Both Methods
- FIFO assumes receipt is the point of purchase recognition.
- CIF costs from invoices must be added to purchase invoices.
By the way, Month-To-Date (MTD) refers to "from the beginning of the month to today," while Year-To-Date (YTD) refers to "from the beginning of the fiscal year to today."
Duality of Quantity and Amount in Inventory Management

"Duality" refers to two sides—front and back—meaning two opposing characteristics. Inventory management also has the duality of quantity and amount, and the inventory amount must be synchronized with the accounting inventory account no later than the end of the month.
Goods become inventory in the warehouse at the time of receipt (after inspection), while the valuation amount is determined at the time of purchase recognition after the invoice arrives. This means that if the timing of receipt and purchase recognition differs, the valuation amount for issuance cannot be determined.
FIFO and the moving average method are inventory valuation methods that require the valuation unit price to be determined at the time of issuance. In the total average method (monthly), the valuation unit price is determined at the end of the month when all receipt amounts for the month are known, but in reality, this occurs at the beginning of the following month when all receipt invoices arrive.
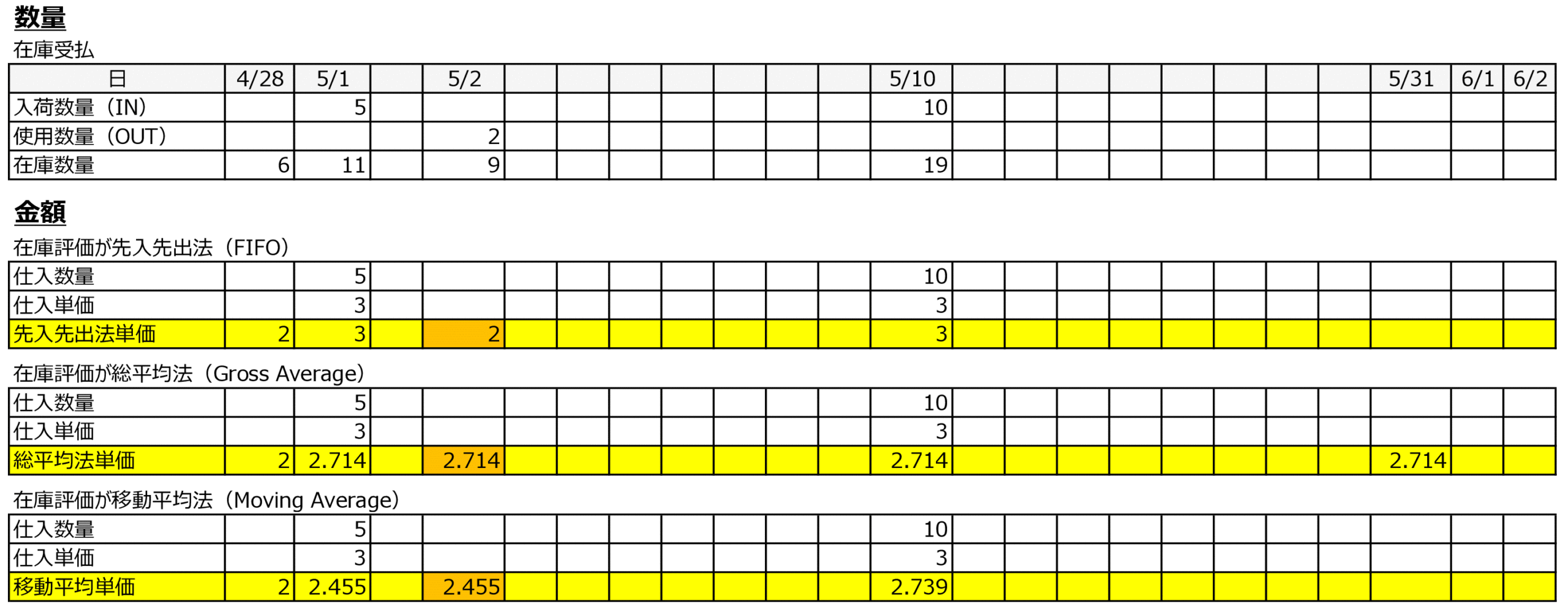
In FIFO or the moving average method, purchase recognition is assumed to be based on receipt, and even if all monthly receipts arrive as a consolidated invoice at the beginning of the next month, purchase recognition must occur at the time of receipt.
- By recording a dummy purchase at the time of receipt, the inventory becomes usable. The D/O (Delivery Order) number is entered as the invoice number, and upon arrival of the consolidated invoice, it is matched and corrected to the invoice number.
- Upon Receipt
(Dr) Purchase (Cr) A/P Accrued - Upon Invoice Arrival
(Dr) A/P Accrued (Cr) A/P
(Dr) VAT-In Prepaid
Since the amount is finalized when the consolidated invoice arrives, if the invoice amount differs from the P/O (Purchase Order) amount, adjustments to the purchase amount and debt amount are necessary.
- Upon Receipt
- At the time of consolidated invoice arrival, all monthly receipts are recorded with the same invoice number, using the first receipt date as the purchase recognition date (risking a reversal of purchase and receipt dates), and monthly issuance records are imported in bulk.
General Ledger Flowchart for Manufacturing
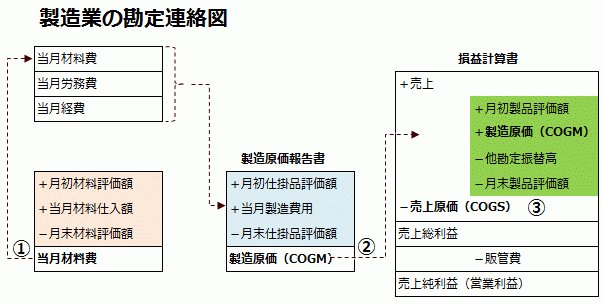
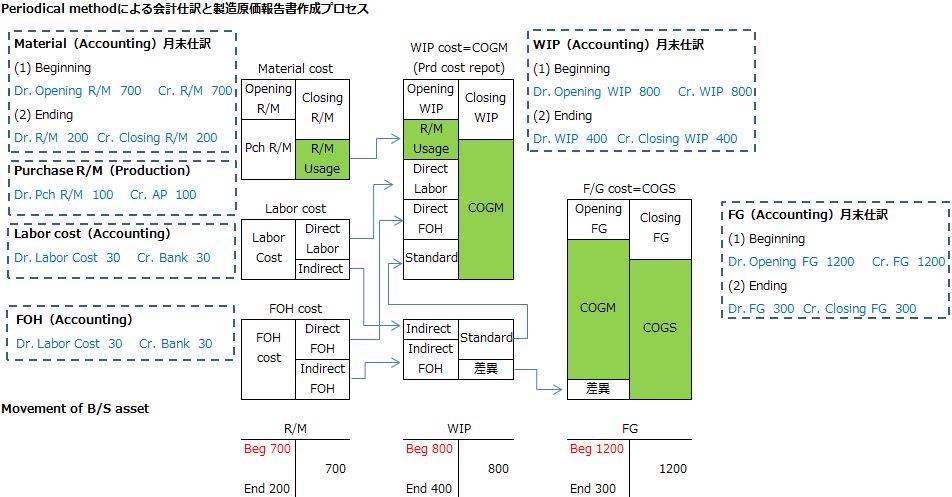
Looking at the ledger flowchart, on the P/L, "Sales - COGS" equals Gross Profit, and COGS is calculated as "Beginning Finished Goods + Monthly Manufacturing Cost - (Other Account Transfers + Ending Finished Goods)."
Monthly Manufacturing Cost (COGM) is "Beginning WIP + Monthly Manufacturing Expenses - Ending WIP," and monthly manufacturing expenses consist of "Material Costs + Manufacturing Labor Costs + Manufacturing Overhead."
Operating Profit is derived by subtracting selling and administrative expenses from Gross Profit, and Ordinary Profit is calculated after considering non-operating income and expenses.
Periodic Method in Accounting Systems
In the periodic method, asset account movements involve transferring the beginning balance to the Opening Stock contra expense account and transferring the ending inventory balance, based on physical inventory, to the Closing Stock contra expense account.
These, along with Purchases, Factory Overhead (FOH), and Labor Costs, are used to determine COGS through periodic method entries.
Periodic Method in Inventory Management Systems
In an inventory management system, the moving average unit price is updated as needed. At month-end, the system finalizes the valuation through a Balance Update process, calculates the total average unit price in a batch, and interfaces the inventory valuation to the accounting system via another Balance Update process.
This mechanism is adopted in ERP systems for non-manufacturing industries, but calculating valuation unit prices that account for procurement-related expenses beyond the cost of purchased goods themselves becomes challenging in the system.
Periodic Method in Cost Management Systems
Materials and purchased parts are calculated using the total average unit price.
By multiplying the total average unit price by the production actual quantity, direct material costs per item (WIP or finished goods) are calculated.
Fixed costs, such as labor costs and factory overhead, are apportioned to items by aggregating the Trial Balance (T/B) balances from indirect departments to cost centers (direct departments or product groups) and then directly allocating them to cost centers.
Rather than inductively calculating material consumption, manufacturing costs, and COGS using the periodic method, the cost management system calculates the monthly material unit price deductively using the total average method to determine material consumption.
On the other hand, fixed costs are inductively apportioned based on direct labor hours and added to the direct material costs of products. The difference lies in calculating COGS as "Product Unit Price × Sales Actual Quantity."
To allocate factory overhead to departments and understand departmental profit/loss in the G/L, indirect labor cost accounts need to be split into molding and processing departments, and manual reclassification entries must be made, requiring department codes to be entered at the time of expensing.
- (Dr) Indirect Labor Cost 10,000 (Cr) Cash 10,000
When performing transfer entries based on allocation calculation results in the cost management system:
- (Dr) Indirect Labor Cost (Molding) 40,000 (Cr) Indirect Labor Cost 40,000
- (Dr) Indirect Labor Cost (Processing) 60,000 (Cr) Indirect Labor Cost 60,000
Perpetual Method in Production Management Systems
In standard actual cost accounting, direct material costs are calculated from the total average unit price determined at month-end, while direct labor costs and overhead are apportioned based on monthly expenses collected from the G/L, using labor hours or output. However, due to the difficulty of achieving rapid accounting in corporate settings, predetermined allocation is permitted under cost accounting standards for actual cost calculation.
Direct material unit prices are updated as needed using the moving average method, and fixed costs are assigned standard unit prices in the item master or Bill of Materials (BOM).
Based on material input actuals, the asset account "Materials" is transferred to the expense account "Material Consumption," and material costs and fixed costs are transferred to WIP via contra accounts. Receipt and issue entries for inputs and production are generated in real-time, reflecting inventory movements in the B/S of the accounting system.
Since fixed costs are finalized at month-end, the product valuation is "Material Usage Amount (Moving Average) + Standard Fixed Costs," requiring adjustment entries for the difference between actual fixed costs and standard costs at month-end.
With each shipment, finished goods are transferred to COGS, keeping inventory, P/L, and B/S synchronized even during the month.
The reason for using the contra account "Material Consumption Offset" instead of directly reducing the asset account "Materials" for material consumption is to obtain the Material Consumption balance from the G/L at month-end.
Upon procurement entry, the inventory asset (materials) for receipts is recorded as actual.
- (Dr) R/M 10 (Cr) A/P 10
Based on input actuals, materials are transferred to material costs. The material unit price determining the valuation is the moving average unit price.
- (Dr) Material Cost 10 (Cr) R/M 10
Monthly manufacturing expenses are transferred via contra accounts based on production actuals. Fixed costs occurring at this point use standard unit prices set in the BOM until actual costs are finalized at month-end, meaning they are first recorded in the contra account for negative expenses.
- (Dr) WIP 10 (Cr) Material Cost-Offset 10
- (Dr) WIP 5 (Cr) FOH-Offset (Cost Credit) 5
- (Dr) WIP 30 (Cr) Labor Cost-Offset (Cost Credit) 30
WIP input amounts are transferred to manufacturing costs.
- (Dr) COGM 45 (Cr) WIP 45
Manufacturing costs are reclassified to finished goods via contra accounts.
- (Dr) F/G 45 (Cr) COGM-Offset 45
Upon sales registration, the inventory asset (F/G) for shipped goods is transferred to COGS.
- (Dr) COGS 45 (Cr) F/G 45
Fixed cost variances are apportioned to finished goods (ending inventory) and COGS based on quantity and recorded.
- (Dr) F/G 0.2 (Cr) FOH-Offset 1
- (Dr) COGS 0.8



