Losses and inventory depletion costs
Losses and Shrinkage are charged to SG&A before they enter the plant and are converted to production costs at the time they enter the plant.
- Before : Manufacturing cost = Work in progress at the beginning of the month + Manufacturing cost of the month (material cost + processing cost) - Work in progress at the end of the month
- After :Manufacturing cost = Work in progress at the beginning of the month + manufacturing cost for the month (material cost + processing cost + work loss cost) - (transfer to other accounts + end-of-month work in progress)
The material cost is put in at the first process and the processing cost is added up at each process, but since the work loss is an extra cost that exceeds the monthly manufacturing cost (material cost + processing cost) that should have been incurred, it should be classified as a separate cost that is neither material cost nor processing cost.
This is Spoilage, which is stated in the P/L using the indirect method of subtracting from the overall manufacturing cost by using a transfer from another account.
On the other hand, in the case of products
- Before : Cost of sales = Products at the beginning of the month + manufacturing costs for the month - products at the end of the month
- After : Cost of sales = products at the beginning of the month + manufacturing costs for the month - (transfers to other accounts + products at the end of the month)
Prototype products are transferred to SG&A expenses through other account transfer account, and it can be said that the amount of prototype products is deducted from the cost of sales.
This can be said to be deducting the amount of the prototype from the cost of sales.
Work in progress and construction in progress
Work-in-process and construction in progress are the same thing, and I think it's only necessary to recognize the difference between them as whether they are for sale or not.
Inventories are sold as products from materials through work in process, but there are items that are not intended to be sold but are purchased as materials and become internal assets as products through work in process.
In accordance with the FOB contract, equipment is recorded in the construction in progress account when it is shipped in Japan and becomes inventory on board, and is capitalized as a fixed asset when it arrives in Indonesia, is brought into the factory and is put into use (the date it is used in the business), and is depreciated based on its useful life.
On the other hand, a die is recorded in a construction in progress account at the time the die materials are purchased and the current surface is machined, and is transferred to a fixed asset and depreciated for accounting purposes at the time the die is made into a finished product through work in progress.
A construction in progress account is convenient because it is like a temporary storage for non-depreciable assets, but if it is not depreciated for a long time, it will be subject to audit.
Criteria for distinguishing between current assets, fixed assets and supplies (cost of supplies)
In Indonesia, as in Japan, current assets are classified into two categories, current assets and fixed assets, and current assets that are to be expensed at the time of consumption are recorded in Supplies or Supplies Expense, and usually no receipts or payments are made in the production management system.
Current assets
- Current assets (cash and deposits)
- Inventories (materials, work in progress, products)
- Deferred assets (research and development costs)
fixed assets
- Property, plant and equipment (amortized by the indirect method using accumulated depreciation)
- Intangible assets (reduced by the direct method)
stored goods
- Dr. Supplies Cr. Cash
- Dr. Supplies Expense Cr. Supplies
In the case of molds, even if their useful life is less than one year, they are classified as category 1 fixed assets because of their high acquisition cost. However, auxiliary molds with a small acquisition cost are sometimes treated as consumables at the time of acquisition, and sometimes they are lumped together with molds and treated as fixed assets.
Since they are fixed assets, they can be recorded as a negative asset using the indirect method. In other words, the cumulative amount of depreciation and loss that has been recognized under the purchase price of the fixed asset of B/S should be written in the B/S.
- Dr. Depreciation 10 Cr. Accumulated depreciation 10
(overhead) (negative asset)
There are two ways of recording molds as fixed assets.
- Recorded in a construction in progress account and transferred to fixed assets when used for business purposes
- Expensed and transferred to fixed assets by transfer to other accounts
The difference between accounting and taxation
The amount of money made by the company is profit for the corporate association and income for the tax association; entertainment expenses recorded on the P/L are not necessarily deductible as an expense (deductible), and tax association expenses may be recorded as an extraordinary gain or loss for corporate accounting purposes when a car that has been written off is sold.
-
- Profit = Revenue - Expenses
- Income = Profit - Loss
You want to reduce taxes by expensing it as soon as possible, but expensing it too early will only result in a negative impact, so you want to amortize it as soon as possible so that your profits are reduced evenly. On the other hand, the tax office wants a longer useful life because if the profit is reduced by expensing, the taxes collected will decrease. This is the difference between accounting (management) and taxation, but it should be preferable to have accounting and taxation managed separately because of the complexity of managing them separately.
On the one hand, the fixed asset system manages the tax accounting, which needs to be classified and properly amortized according to the tax laws related to fixed assets, but on the other hand, the tooling management system manages the amortization based on actual shots on the manufacturing floor, which will reduce the loss on disposal of fixed assets associated with the disposal or sale of fixed assets that occur within the amortization period. The miscellaneous income (residual value) can be calculated automatically.
In the actual accounting process of the accounting department, the valuation calculated in the fixed asset management system and the valuation calculated in the mold management system are managed separately.
Functions of the mold management system
The core of the tooling management system is amortization management based on life cycle management, and in the case of in-house manufactured molds, good receipt is generated upon completion and in the case of purchased molds, good issue is generated based on the actual shot results of the press and molding. to calculate the amortization amount.
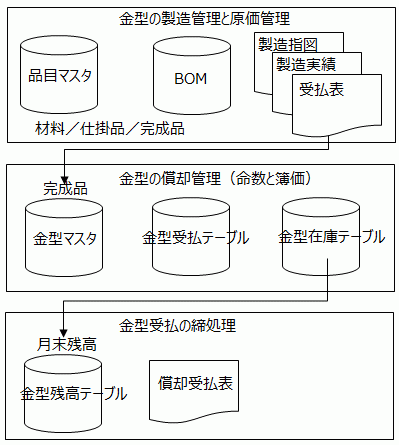
In the case of in-house molds, the actual receipt and payment results from mold materials to work-in-process and finished products are managed, and as with normal inventory, cost is calculated after the monthly closing process.
For finished molds, the standard number of orders, unit price of material and standard processing unit price are stored in the mold master, and the actual receipt and disbursement results (receipt/completion/shot) are recorded in the mold receipt and disbursement table, and the latest information is stored in the mold inventory table.
At the end of the month, the closing process is carried out and tightening information is stored in the mold balance table (balance master). The residual book value of the mold is carried forward to the beginning of the next month as the balance at the beginning of the month.
The system is similar to the fixed asset management system in that it manages receipts and payments, and when a revision is made to the history, it is necessary to recalculate the amortization of the history in a chronological order.


