Material costs and processing costs incurred at the manufacturing site are the current month’s incurred costs. The costs incurred to produce the products themselves are manufacturing costs (incurred costs based on production quantity), while the costs incurred to produce the products sold are the cost of sales (incurred costs based on shipped quantity). Selling and administrative expenses incurred for sales are deducted from gross profit. Cost Management in Indonesia Mass production factories, such as two- and four-wheeler parts manufacturers common in Indonesia, have multiple manufacturing processes. In such cases, processing costs are calculated for each process, and the method of aggregating these costs into the product is called process costing. In this approach, labor costs and manufacturing overheads are recorded at the end of the month by the accounting department, transferred to inventory assets, and then allocated accordingly. On the other hand, in factories producing custom-made items under individual order production, job order costing is used, where costs are aggregated by order number or project number. In this case, ... 続きを見る

Key Points for Conducting Accounting Interviews in Indonesia
I’m working on business system implementation in Indonesia, and I collaborate with a diverse group of Indonesian staff—some excel at production management, others at accounting, and some at programming. After working together for a long time, I’ve come to realize, albeit belatedly, that the way we grasp the essence of the same problems we face differs.
This might sound rigid, but even though the essence of things is singular, the way it’s articulated varies depending on the “key points” of understanding, and I believe the approach to grasping that essence differs from person to person.
It’s fine for people to have different ways of understanding the same reality, and when I discover that someone else’s way of perceiving the essence differs from how I’d express it, I find it somewhat moving.
Unlike those in the accounting department who deal with corporate accounting daily, I interact with accounting in the unique context of accounting system implementation. When hearing practical accounting matters from clients, I abstract it into a rather global definition: “Accounting is the rearrangement of numbers within the rules of the trial balance equation.”
- Assets + Expenses = Liabilities + Net Assets + Revenue
This equation holds because the profit, which is the difference between expenses and revenue in the income approach, becomes the increase in net assets in the property approach. This is the foundation of my accounting knowledge.
Without this understanding, I couldn’t explain the cost of sales or period costs.
Transferring Three Accounts—Beginning Inventory, Monthly Purchases, and Ending Inventory—to the Cost of Sales Account
Recording purchases as they happen means not managing them as assets in accounting during the month. Thus, at month-end, you need to transfer the beginning and ending inventory amounts to synchronize inventory with accounting.
If you don’t do this, you can’t create a B/S, right? 
The contra accounts for this inventory transfer (expense contra accounts), Opening Stock (expense) and Closing Stock (negative expense), fall under P/L items.
- Total Revenue − Total Expenses = Total Profit
This way, total profit can ultimately be confirmed from the trial balance amounts, but on the P/L, gross profit must be explicitly stated.
- Sales − Cost of Sales = Gross Profit
To record this, you need to determine the ending inventory amount and transfer a portion of total expenses to the cost of sales by offsetting it against the beginning inventory and monthly manufacturing costs.
- Opening Stock + Monthly Purchases − Closing Stock = Cost of Sales
This means zeroing out the balances of the three accounts—Opening Stock, Closing Stock, and monthly purchases—eliminating them from the P/L, and setting the difference as the balance of the cost of sales account.
For a non-manufacturing example, if you record a 20-yen purchase as an expense in the purchase account but don’t sell a single unit, the cost of sales under the three-way method is naturally 0.
- Beginning Inventory (0) + Monthly Purchases (20) − Ending Inventory (20) = Cost of Sales (0)
If there’s no need to list the cost of sales on the P/L, total profit is calculated as the difference between Opening Stock (debit expense) and Closing Stock (credit expense), the contra accounts when transferring beginning and ending inventory.
On the other hand, if you record purchases as assets and don’t sell any, there’s no chance to transfer them to the cost of sales, so naturally, the cost of sales is 0.
In this case, since the goods are already recorded as assets, inventory and accounting are synchronized, so there’s no need to transfer beginning and ending inventory.
Under the major premise that the P/L is only generated at month-end, expensing purchases at the time of acquisition means inventory transfers occur at month-end to calculate total profit. Further applying the three-way method to calculate the cost of sales allows the expenses for sold items to be clearly separated on the P/L.
- The difference between total revenue and total expense items is total expense:
Total Revenue − Total Expenses = Total Profit - Transfer beginning and ending inventory to Opening Stock and Closing Stock accounts:
(Total Revenue + Closing Stock) − (Total Expenses + Opening Stock) = Total Profit
⇒ The difference between beginning and ending inventory goes to asset changes - Separate total revenue into sales and other revenue, and total expenses into purchases and other expenses:
Sales − (Opening Stock + Monthly Purchases − Closing Stock) + (Other Revenue − Other Expenses)
Timing of Selling/Admin Expenses and Cost of Sales
Selling and administrative expenses are fully expensed in the month they occur, but products are expensed (turned into cost of sales) only for the sold portion—at shipment (in perpetual recording) or month-end (in the three-way method)—with the remainder staying as ending inventory assets.
When expensing at month-end, you transfer a portion of total expenses to the cost of sales within the total expenses and manage it separately from selling/admin expenses on the P/L.
Whether you expense purchases by recording them in the purchase account and synchronize inventory with accounting at month-end using the expense contra accounts Opening Stock and Closing Stock, or record purchases as assets in the goods account and expense them as cost of sales when sold, the total profit on the month-end P/L remains the same.
If purchases are recorded in the purchase account and nothing is sold, the inventory transfer at month-end (beginning and ending inventory) increases inventory and reduces the cost of sales. Ultimately, this matches the cost of sales and profit on the P/L when expensing only upon sale.
In short, expensing at purchase and turning it into cost of sales at month-end versus recording as assets at purchase and turning it into cost of sales upon sale is merely a difference in the timing of when it becomes cost of sales.
No modern corporate accounting considers all incurred expenses as period costs and deems it sufficient to know only the total profit calculated as total revenue − total expenses. Calculating the cost of sales and preparing the P/L is essential.
The perpetual method—recording purchases as assets and transferring to cost of sales with each sale—is convenient for tracking inventory valuation in accounting during the month. However, expensing purchases at acquisition and transferring beginning and ending inventory at month-end doesn’t allow mid-month inventory valuation in accounting. Still, it excels at reflecting monthly physical inventory counts in accounting, metabolizing assets to align numbers with reality.
Relationship Between Manufacturing Cost and Cost of Sales
Manufacturing cost is the monthly manufacturing cost unit price multiplied by the number of products received in the warehouse, while cost of sales is the beginning product inventory unit price or monthly manufacturing cost unit price multiplied by the shipped quantity.
Using the total average method, the direct material cost (variable cost) unit price is calculated, and fixed cost unit prices are accumulated by process based on allocation rules tied to direct labor time or production quantity, determining the manufacturing cost unit price via the roll-up method (cumulative method).
- Manufacturing Cost = Product Manufacturing Unit Price × Production Quantity
- Manufacturing Cost = Beginning WIP + Monthly Incurred Costs − Ending WIP
The cost of products shipped to customers in the month is the cost of sales, but the unit price differs between beginning product inventory and monthly manufactured products.
- Cost of Sales = Beginning Product Inventory Unit Price × Shipped Quantity + Monthly Manufacturing Cost Unit Price × Shipped Quantity
- Cost of Sales = Beginning Product Inventory + Monthly Manufacturing Cost − Ending Product Inventory
If all products manufactured in the month are shipped and no ending inventory remains, the product unit price is the manufacturing cost unit price, and since warehouse receipt quantity equals shipped quantity, manufacturing cost and cost of sales become identical.
Product Value Breakdown as Cost of Sales vs. Expenses for Selling as Selling/Admin Expenses
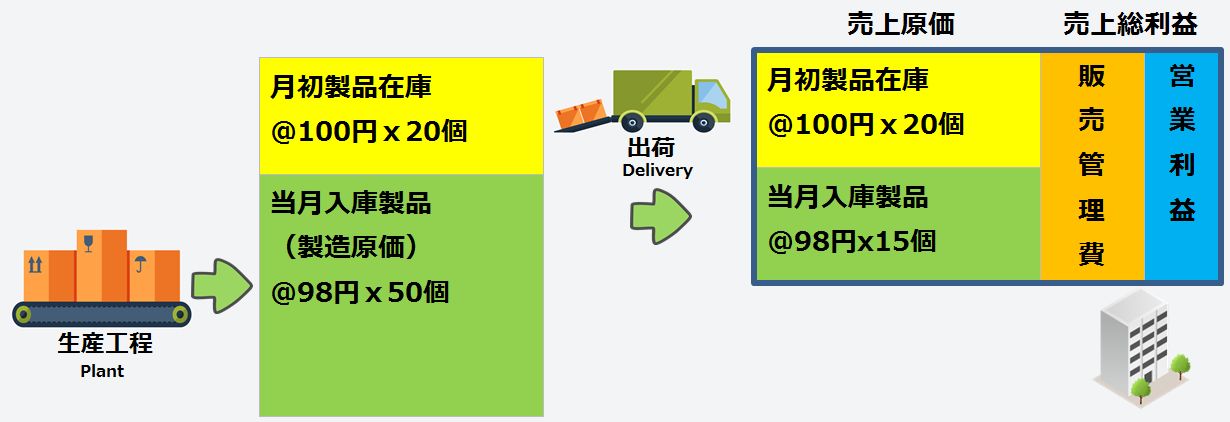 The cost of sales is the expense incurred to manufacture the products sold, excluding costs for selling or management. These selling and administrative expenses are deducted from gross profit.
The cost of sales is the expense incurred to manufacture the products sold, excluding costs for selling or management. These selling and administrative expenses are deducted from gross profit.
In Indonesia, there are two main accounting entry patterns for material purchases:
- Record in the materials account (asset) and expense only the used portion (monthly material cost):
(This can be expensed continuously as used or in a lump sum at month-end like stored goods.) - Record in the purchase account (expense), expense the beginning material inventory (positive expense), and deduct the ending material inventory (negative expense) to calculate monthly material cost:
(Strictly speaking, the purchase account has a strong asset-like nature as a prepaid expense.)
Materials are expensed only when sold, but selling and administrative expenses are expensed when incurred in the relevant accounting period, hence called period costs.
Relationship Between Cost of Sales and Gross Profit
Back when I ran a boutique in Bali, I’d buy clothes from Jakarta and sell them in Bali. The purchase price of the clothes was the cost of sales, and subtracting the cost of sales from sales gave the gross profit (marginal profit), i.e., gross profit. True Story! Learning About Marginal Profit and Break-Even Point from My Boutique Management Experience in Bali Costs can be divided into variable costs and fixed costs. The break-even point sales, which recover fixed costs, are determined by the marginal profit rate—the ratio of the purchase price (variable cost) to sales. In other words, direct costing calculates how many clothes need to be sold to achieve the break-even point sales, considering only variable costs as the original cost. 続きを見る

Gross profit, also called gross margin, includes direct and indirect labor costs in manufacturing as part of the cost of sales.
In retail, a common saying is, “Management is the act of recovering fixed costs (employee salaries, tenant rent) with gross profit.”
The reason labor costs in manufacturing are included in the cost of sales while those in retail are not is that the former are labor costs to produce products, and the latter are labor costs to sell products.



