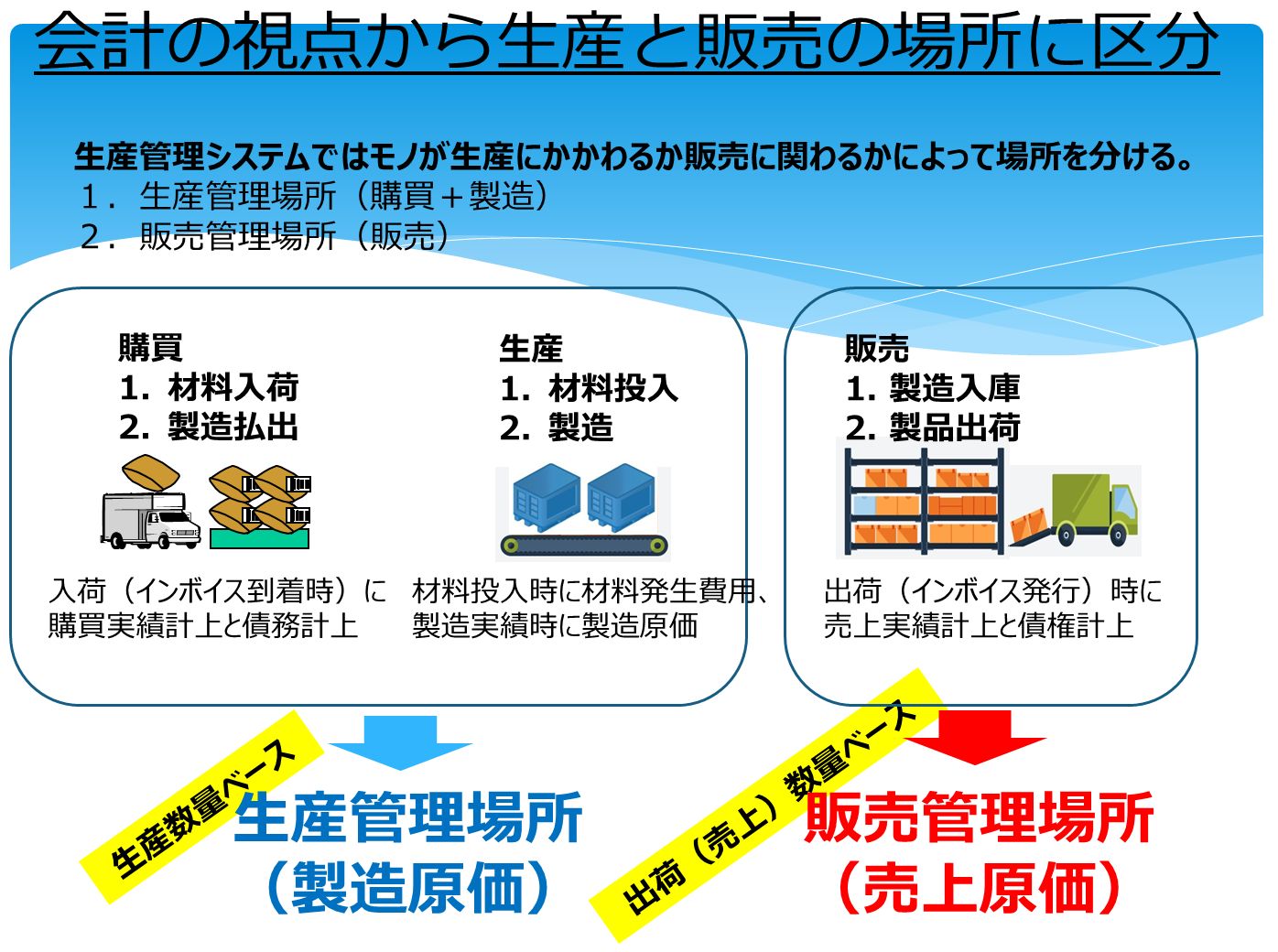
Separation of production management and sales management
The cost of production can be calculated based on how many products and how much it costs to produce a product in the current month, and the cost of goods sold and shipped can be calculated based on the results of sales management.
- Gross average product unit price = (product inventory at the beginning of the month + product manufacturing cost of the month) / (product volume at the beginning of the month + manufacturing volume of the month)
- Cost of Sales = Total Average Product Unit Price x Shipping Volume
To calculate cost of sales, we need sales management's actual shipments, and to calculate gross profit, we need sales management's actual sales.
- Sales - Cost of sales = Gross profit
Two perspectives: inventory control and cost control
When looking at the two aspects of inventory and cost, the plant can be broadly divided into three main locations, and the departments that have jurisdiction over those locations (warehouses) generally differ.
- Materials warehouse (RM warehouse): Purchasing department keeps track of incoming goods
- Plant: Production department manages input and production performance
- Finished good warehouse: The logistics department (sales department) manages the shipment performance
In other words, in order to calculate manufacturing costs, we need the following information that the purchasing and manufacturing departments have
- Beginning of the month inventory of the material warehouse
- Material warehouse receipts
- Inventory at the beginning of the month in the manufacturing process
- Production Process Input Results
- Production results of the manufacturing process
In order to calculate the cost of sales, you will also need the following information that the logistics department (sales department) has
- Product warehousing inventory at the beginning of the month
- Product warehousing results
- Product Warehouse Shipment Results
And in order to calculate both the cost of production and the cost of sales, you need all the information that the purchasing department and the manufacturing and logistics departments (sales department) have.
All incoming and outgoing data and inventory data are maintained with departmental information
All incoming and outgoing data in the business system holds the generating department, and the inventory data that goes into the warehouse as a result of the incoming and outgoing data also holds the departmental information that manages the warehouse as a location.
In a physical organization, each department's data in Excel format will be sent to you by email, and then merged together.
In the same way, the performance data managed in the production management system is also compiled by department, so it is necessary to convert the separate department codes into a common department code in order to merge and calculate the gross profit.
The departments (purchasing, manufacturing, and sales) involved in the receipt and payment of production management systems are the main entities on the organizational chart that control where inventory is placed, but in accounting and cost control systems, lines and product groups are the aggregate units, depending on the purpose.
In the system, a general department that does not really exist is set up for the purpose of cutting forms and dividing authority, or a fictitious common department is set up to record expenses that cannot be borne by a specific department.


