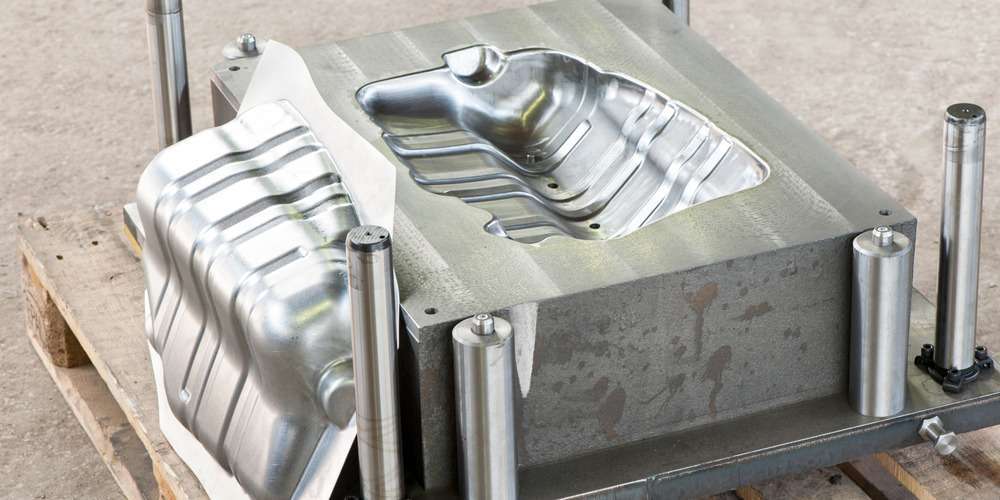
The number of molds available, setup time for mold changes, mapping between molds and resources, and maintenance schedules significantly impact production plans based on primary resources. Sub-resources, such as workers or molds, which act as constraints on primary resources, can be reflected in the production plan. Production Scheduler in Indonesia In Indonesia's Japanese manufacturing industry, the adoption of production management systems has been increasing. However, when it comes to one of the key challenges in production management—creating feasible production plans that take machine and equipment loads into account—manual work using Excel remains the standard practice. As a result, the demand for production schedulers is expected to grow in the future. 続きを見る

Setting Mold Constraints and Internal/External Setup
By setting sub-resources in the manufacturing BOM and assigning 0 or blank to the pre-setup tasks for both primary and sub-resources, no pre-setup time is incurred, but it can express that only the constraint of mold availability exists.
If the mold change time is set as the pre-setup time for the primary resource, it becomes an internal setup (setup performed by stopping the line or machine). For example, setting 120 minutes for the pre-setup task of the primary resource CUT and 0 for the sub-resource means the machine stops for 120 minutes of internal setup time.
Conversely, if the mold change time is set as the pre-setup time for the sub-resource, it becomes an external setup (setup performed without stopping the line or machine). For instance, setting the primary resource’s pre-setup task as blank and the sub-resource’s pre-setup task as 120 minutes means the machine continues operating during the 120-minute external setup time.
Worker Constraints and Adjusting Planned Operation Time Based on Resource Quantity
Like molds, workers can be considered sub-resources and reflected as constraints on the primary resource’s plan. In this case, a conditional expression for worker availability is set in the resource validity condition of the sub-resource (worker).
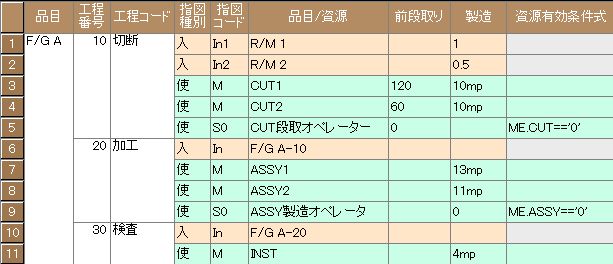
For operations (pre-setup tasks or manufacturing tasks) in a process, workers are assigned as sub-resources to the primary resource. The number of workers is adjusted via the resource quantity in the calendar, and the resource quantity constraint in the resource table is varied accordingly, reflecting it in the planned operation time.
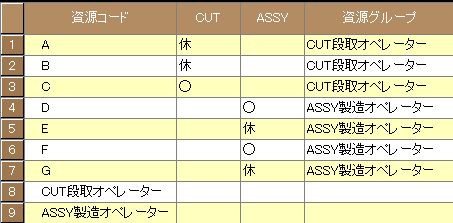
- Set the sub-resource (worker) for the relevant process in the manufacturing BOM.
- Set the worker’s resource constraint in the resource table to infinite capacity.
- Increase the resource quantity in the calendar table while monitoring the load status.
Ample Equipment Capacity with Constraints on Assignment Order
“Even with ample equipment capacity, the influence of limited sub-resources like molds or workers affects the production plan” can be rephrased as “By setting sub-resources, constraints can be placed on the assignment order of the equipment’s production plan.”
A production scheduler assigns operations to available equipment to create a plan that completes in the shortest time when equipment capacity is sufficient. However, if there’s a constraint like “The next lot cannot start until the previous lot is completed,” setting a common sub-resource for the production processes of both lots enables a serial production plan.



