In standard cost accounting, not only direct material costs (things), which are variable costs, but also direct labor costs (people) and manufacturing overhead costs (machines), which are typically fixed costs, are treated as if they were variable costs. Then, material costs are analyzed into price variance and quantity variance, labor costs into wage rate variance and labor hour variance, and overhead costs into efficiency variance, capacity variance, and budget variance. Cost Management in Indonesia Mass production factories, such as two- and four-wheeler parts manufacturers common in Indonesia, have multiple manufacturing processes. In such cases, processing costs are calculated for each process, and the method of aggregating these costs into the product is called process costing. In this approach, labor costs and manufacturing overheads are recorded at the end of the month by the accounting department, transferred to inventory assets, and then allocated accordingly. On the other hand, in factories producing custom-made items under individual order production, job order costing is used, where costs are aggregated by order number or project number. In this case, ... 続きを見る

Variance Analysis in Actual Cost Accounting vs. Standard Cost Accounting
In Standard Costing, Direct Labor Costs and Manufacturing Overhead Are Calculated as Variable Costs
Manufacturing costs are broadly categorized into direct material costs (things), direct labor costs (people), and manufacturing overhead costs (machines). The majority of variable costs consist of direct material costs and outsourcing processing fees, but manufacturing variable costs (direct expenses) also include some manufacturing overhead items such as utility costs for machines, shipping costs for specific items, and purchasing incidentals.
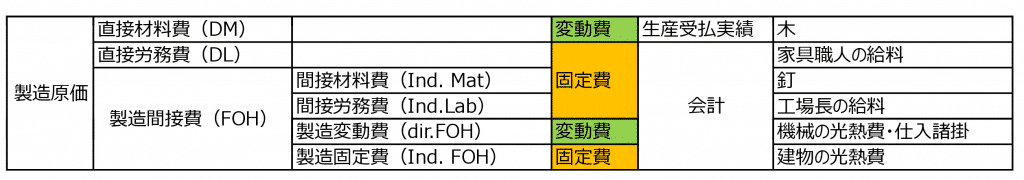
In addition to direct material costs, which are variable costs, direct labor costs and manufacturing overhead costs, which are fixed costs, are expressed in a variable cost-like formula to calculate standard costs.
- Direct Material Cost = Unit Price × Quantity
- Direct Labor Cost = Wage Rate × Labor Hours
- Manufacturing Overhead = Allocation Rate × Operating Hours
Direct Material Costs (Things)
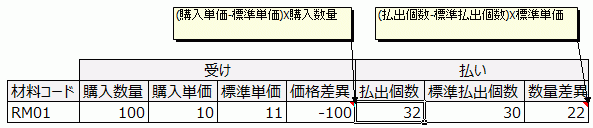
Production management systems function based on master data such as item masters, BOMs (Bill of Materials), and unit price masters. However, in daily operations on the shop floor, things don’t always align perfectly with the definitions in the master data.
For example, the actual material input on the shop floor may exceed the required amount based on the BOM, scrap may occur leading to production results falling short of the plan, or the purchase price at the time of issuing a P/O (Purchase Order) may end up lower than the price in the purchasing unit price master due to negotiations. These create variances between master data and actual shop floor performance.
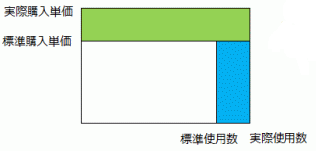
This example illustrates variances related to direct material costs: quantity variance (Qty difference) and price variance (Price difference).
- Price Variance = (Actual Purchase Unit Price - Standard Purchase Unit Price) × Actual Quantity
- Quantity Variance = (Actual Quantity - Standard Quantity) × Standard Purchase Unit Price
The practical document format looks something like this:
Direct Labor Costs (People)
For direct labor costs, actual working hours (activity) per process step are collected via daily work reports, and:
- Actual Direct Labor Cost ÷ Actual Working Hours
The variance caused by the difference between the actual wage rate derived from this and the standard wage rate (allocation rate) is called the wage rate variance (Allocation rate difference), while the variance caused by the difference in working hours is called the labor hour variance (Activity difference).
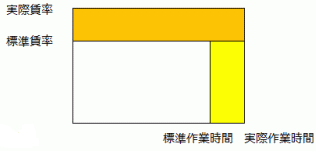
- Wage Rate Variance = (Actual Wage Rate - Standard Wage Rate) × Actual Working Hours
Actual Wage Rate = Actual Direct Labor Cost ÷ Actual Working Hours - Labor Hour Variance = (Actual Working Hours - Standard Working Hours) × Standard Wage Rate
The practical document format looks something like this:
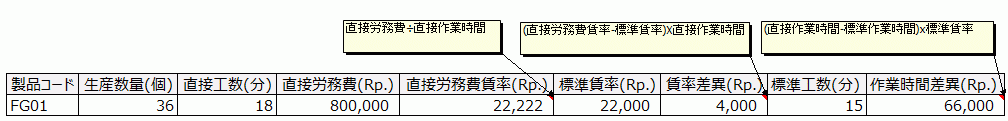
Actual working hours (direct labor hours) can be aggregated by direct department units (cost centers). However, to calculate direct labor hours per item (minutes per unit), they are apportioned based on standard labor hours (Standard activity) preset in the master data and the actual production quantity.
- Total Direct Labor Hours per Item = Total Direct Labor Hours by Department × {(Standard Labor Hours × Actual Production Quantity) / SUM(Standard Labor Hours × Actual Production Quantity)}
The concept of calculating direct labor cost per unit as “Labor Hours × Wage Rate” is used by the ordering party to provide an estimate of outsourcing processing fees to the contractor, but it is also applied when calculating labor costs per product.
Manufacturing Overhead Costs (Machines)
While the majority of variable costs in manufacturing costs consist of direct material costs and outsourcing processing fees, strictly speaking, utility costs for operating machines should be classified as variable costs. Thus, manufacturing overhead costs are divided into manufacturing variable costs and manufacturing fixed costs.
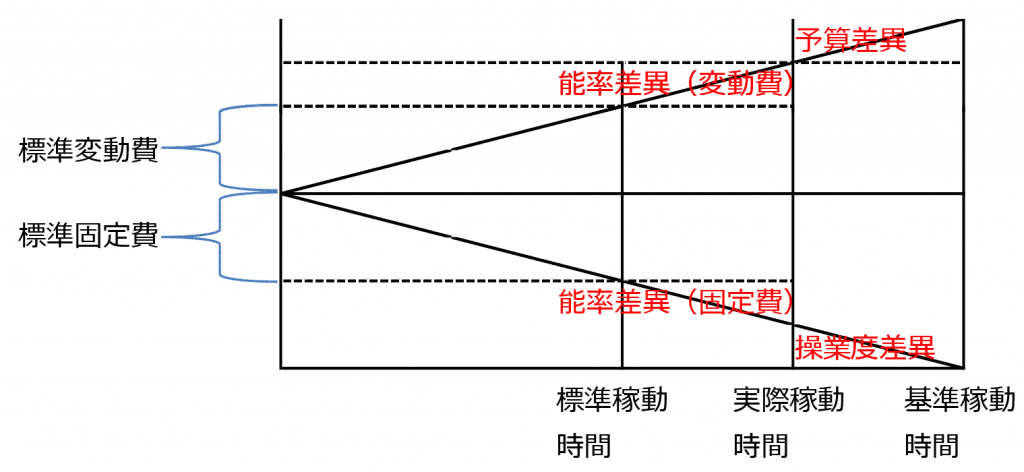
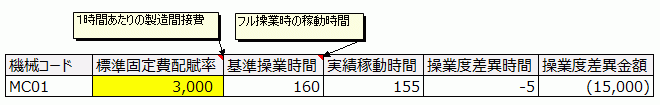
The difference between standard operating hours (full capacity hours) and actual operating hours is the capacity variance hours. When multiplied by the standard fixed cost rate, this becomes the capacity variance amount, representing the loss when machine load (Load) falls short of capacity (Capacity).
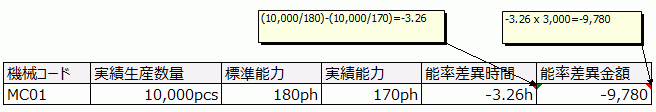
On the other hand, efficiency variance represents the loss when the actual machine capacity falls short of the standard capacity. The difference between the standard capacity hours (actual production quantity divided by standard capacity) and the actual capacity hours (actual production quantity divided by actual capacity) is the efficiency variance hours. When multiplied by the standard fixed cost rate, this becomes the capacity variance amount.
Budget variance is the difference when actual manufacturing overhead costs (allocation rate × actual operating hours) exceed the budget due to increases in material unit prices or wage rates.
Differences Between Actual Cost Accounting and Standard Cost Accounting
In actual cost accounting, the total direct material cost is calculated as “Standard Material Unit Price × Actual Input Quantity,” and the total manufacturing overhead cost is calculated as “Standard Unit Price (per hour) × Actual Working Hours.” This allows real-time calculation of unit costs for products and intermediates (preliminary costs). In accounting system-integrated ERP packages, journal entries are recorded using the perpetual inventory method, enabling constant tracking of inventory valuation.
For material costs in standard costing, when “Standard Usage = Child Requirement (BOM) × Production Quantity,” it is:
- Standard Purchase Unit Price (Purchasing Unit Price Master) × Standard Usage
However, in actual costing, it becomes:
- Standard Purchase Unit Price (Purchasing Unit Price Master) × Actual Usage
For example, when producing 100 units of a product that uses 4 bolts per unit, in standard costing:
- Standard Purchase Unit Price × 4 Bolts × 100 Units
But in actual costing:
- Standard Purchase Unit Price × (4 Bolts × 100 Units + Defectives)
In other words, while there is no price variance between actual and standard costs, a quantity variance arises as Standard Purchase Unit Price × Variance Amount.
Similarly, for labor costs in standard costing:
- Standard Wage Rate × Standard Working Hours
But in actual costing:
- Standard Wage Rate × Actual Working Hours (Standard Working Hours + Loss Time)
Thus, while there is no wage rate variance, a labor hour variance occurs.



