It is said that a company’s internal reserves are not necessarily held as cash or deposits because, even though transferring profit/loss to retained earnings increases net assets, the accounts receivable, which are the substance of revenue, will eventually turn into cash or deposits. Meanwhile, the balance decreases due to capital expenditures or loan repayments, independent of the movements in net assets. Accounting System in Indonesia The cloudification of accounting systems is advancing in Indonesia, with the three major local cloud systemsAccurate, Zahir, and Jurnalleading the market. However, in reality, it is said that fewer than 8% of domestic companies have implemented accounting systems. This is why new cloud-based accounting systems continue to be launched in what might seem like an already saturated Indonesian market. It suggests that both domestic and international IT startups see significant potential for cloud accounting systems to expand their market share locally. In Indonesia, automated journal entries due to the widespread use of accounting systems have become commonplace, and over the ... 続きを見る

Net Assets Section of the Balance Sheet (B/S)
Net assets are recorded in the net assets section of the Balance Sheet (B/S) in one of the following forms: Legal Capital, Legal Capital Surplus, or Retained Earnings (also known as Earned Surplus). Legal Capital Surplus and Retained Earnings constitute internal reserves.
For companies with significant growth potential and many investment opportunities, rather than returning profits to shareholders through dividends, they aim for growth through reinvestment, such as purchasing fixed assets like equipment. To achieve this, they bolster internal reserves by carrying forward profits as Retained Earnings, thereby increasing the cash and deposit balance.
Additionally, under Indonesian company law, from the perspective of creditor protection, there is an obligation to accumulate Legal Capital Surplus up to 20% of Legal Capital (in Japan, the combined total of Legal Capital Surplus and Retained Earnings must reach 25% of Legal Capital).
Japan is said to be experiencing a deflationary recession, a state where companies hold excess internal reserves without injecting money into the market, resulting in stagnant wages and prices.
Prime Minister Abe’s Liberal Democratic Party administration set an inflation target of 2% through the Bank of Japan to overcome the deflationary mindset. This was precisely to encourage the release of internal reserves (Legal Capital Surplus and Retained Earnings in accounting terms), raise prices, boost consumer spending, increase sales, improve corporate sentiment, and create a cycle where companies borrow money.
Indeed, if liquid assets accumulated in companies due to investment restraint and wage freezes during the "lost decade," it might be possible to "release internal reserves" by raising wages. However, companies have endured bad economic conditions by keeping wages flat, so the idea of raising wages to improve the economy doesn’t quite resonate.
Moreover, even if there were cash reserves for this purpose, the net profit for the period belongs to investors. Management cannot arbitrarily use it to fund wage increases without approval from shareholders at a general meeting.
There are three types of people involved in a corporation:
There are four ways to handle the resulting profits, but how management actually handles them is something investors can influence at the shareholders’ meeting:
- Return to investors (dividends)
- Invest
- Improve worker conditions (wage increases)
- Do nothing (accumulate as internal reserves)
Since internal reserves are not necessarily held as cash or deposits, whether "releasing internal reserves" is feasible depends on the company’s financial situation.
For example, a printing company that invested its 1 million yen deposit in an additional 5 million yen printing machine might have internal reserves on its financial statements but zero cash.
B/S after continued investment in printing machines:
- (Dr) Deposits 1,000,000 (Cr) Legal Capital 2,000,000
- (Dr) Printing Machine 10,000,000 (Cr) Legal Capital Surplus 7,000,000
- (Cr) Retained Earnings 2,000,000
Purchasing an additional printing machine for 5 million yen:
- (Dr) Printing Machine 5,000,000 (Cr) Borrowings 4,000,000
- (Cr) Deposits 1,000,000
In accounting terms, transfer entries occur each month if profit appropriation is performed, but in an accounting system, this isn’t something you need to consciously manage. At the annual closing, the system automatically transfers the amount to the target net assets account (Retained Earnings), and entries are created for processes like allocating accumulated internal reserves to dividends.
- (Dr) Net Profit 800,000 (Cr) Retained Earnings 800,000
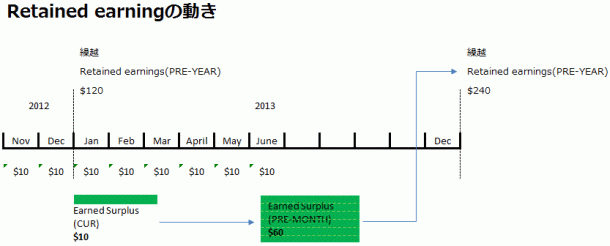
In Indonesia, it’s rare to appropriate net profit for the month at each month-end closing; if it happens, it’s typically done at quarterly closings. Before reaching the final Retained Earnings (Carried-Forward Retained Earnings) on the B/S, temporary profit/loss accounts are used monthly or periodically.
- RETAINED EARNINGS (CUR) – Retained Earnings (Current Month Net Profit)
A temporary profit/loss account used to transfer monthly Net Income to RETAINED EARNINGS (PRE-MONTH). - RETAINED EARNINGS (PRE-MONTH) – Retained Earnings (Cumulative Net Profit from Period Start to Previous Month)
A temporary profit/loss account used to transfer the period-end balance to RETAINED EARNINGS (PRE-YEAR) at the start of the next year. - RETAINED EARNINGS (PRE-YEAR) – Carried-Forward Retained Earnings (Cumulative Net Profit from Inception to Previous Year)
Commonly referred to as Retained Earnings, this is the cumulative total from the inception year to the previous period, representing the accumulated after-tax profits from past P/L statements.
Eliminating Cumulative Losses
If production actuals are not correctly entered into the system or month-end inventory counts are inaccurate, monthly inventory differences fluctuate significantly. A negative inventory difference increases manufacturing costs (or COGS for finished goods), resulting in a loss, while a positive difference reduces manufacturing costs (or COGS), resulting in a gain.
Since the system operates in a logical realm, inventory differences are reflected as inventory shrinkage costs (selling & administrative expenses) in COGS, directly impacting the P/L. Instead of expensing monthly losses from inventory differences, booking them as another asset can "hide input errors" (not losses), temporarily improving the appearance of the B/S and P/L.
Possible methods for handling inventory differences include:
- Expense monthly and reflect in COGS
- Revalue fixed assets and transfer to revaluation gains
- Record Retained Earnings as negative
- Transfer to a temporary account (asset)
Ideally, when inventory differences occur, you’d trace receipt/issue actuals, correct the data, apply method 1 to minimize expensing differences, and record negative Retained Earnings for losses using method 2. However, if this is labor-intensive, the system allows temporarily transferring losses to method 3 for later processing.
Ultimately, some form of transfer to an account is necessary, likely requiring a capital reduction to restructure the B/S.
Cumulative losses accumulate negatively in Retained Earnings, so if Assets – Liabilities = Net Assets is negative, it indicates insolvency. However, banks may still lend, and stock prices may rise due to:
- Extremely high future potential of the company
- Profitability of the group as a whole
- Vast personal assets of the owner
- Significant unrealized gains in assets
Thus, it’s not necessarily dire to have cumulative losses.
Significance of Transferring Beginning and Ending Inventory at Closing
In closing entries, all monthly expense and revenue accounts are transferred to the profit/loss account, with two types of expenses targeted:
- Period expenses incurred and expensed in the current month
- COGS, calculated as beginning inventory plus monthly purchases minus ending inventory
The entire beginning inventory is transferred to the Opening Stock expense account, purchases are fully recorded as an expense account upon receipt (creating an over-expensed state), and the portion remaining in ending inventory is transferred back to assets, deducting it from expenses to derive the incurred expense (COGS).
- Replace inventory on the Balance Sheet (B/S) and deduct the ending inventory portion from purchases
(Dr) Opening Stock 800 (Cr) Inventories 800
(Dr) Inventories 1000 (Cr) Closing Stock 1000
The balances of the Opening Stock, Closing Stock, and Purchase accounts are zeroed out on the P/L, replaced by the difference recorded as the COGS account balance (expense for sold items).
- Transfer beginning inventory, monthly purchases, and ending inventory to COGS
(Dr) COGS 800 (Cr) Opening Stock 800
(Dr) Closing Stock 1000 (Cr) COGS 1000
(Dr) COGS 400 (Cr) Purchases 400
This completes the preparation for transferring expense accounts to the profit/loss account.
Net Profit Transferred to Retained Earnings Does Not Remain as Cash or Deposits
After month-end closing, the profit/loss on the P/L is recorded as is on the B/S under the profit/loss account (Net Profit). At the annual profit appropriation, it is either distributed as dividends or retained as Retained Earnings.
In system accounting, figures aggregated from journal entries recorded in the General Ledger (G/L) are pasted into pre-prepared formats to create the P/L and B/S. In bookkeeping terms, all monthly expense and revenue accounts are transferred to the profit/loss account.
- Transfer all expense accounts to profit/loss
(Dr) Profit/Loss (Net Income) 80 (Cr) Total Expenses 80 - Transfer all revenue accounts to profit/loss
(Dr) Total Revenues 100 (Cr) Profit/Loss (Net Income) 100
Companies expecting growth bolster internal reserves for reinvestment in fixed assets like equipment, rather than returning profits to shareholders via dividends.
- Transfer the surplus (credit) balance of the profit/loss account to Retained Earnings
(Dr) Profit/Loss (Net Income) 20 (Cr) Retained Earnings 20
Transferring profit/loss to Retained Earnings increases net assets, but the accounts receivable, the substance of revenue, eventually become cash or deposits. The balance decreases due to capital expenditures or loan repayments, independent of the net assets’ movements.
- Capital expenditure
(Dr) Machinery 5 (Cr) Cash/Deposits 5
A few years ago, in response to the opinion in Japan that "corporate internal reserves should be released to end deflation," the counterargument was, "Internal reserves are not necessarily held as cash or deposits," and this is why.
Methods of Profit Appropriation
Net assets are presented on the B/S as Legal Capital, Legal Capital Surplus, or Retained Earnings (Earned Surplus). Legal Capital Surplus and Retained Earnings constitute internal reserves, and under Indonesian company law, Legal Capital Surplus must be accumulated up to 20% of Legal Capital for creditor protection.
Dividends to shareholders as part of profit appropriation are sourced from Retained Earnings and recorded as a liability under unpaid dividends.
- Dividend from profit reserves
(Dr) Retained Earnings 10 (Cr) Unpaid Dividends 10
(Dr) Unpaid Dividends 10 (Cr) Cash/Deposits 10



