In standard costing, planned production quantities are calculated from the product production plan and BOM, planned direct labor time is calculated from the planned production quantities and the standard cost efficiency master, allocation rates are calculated from the manufacturing overhead budget and planned production quantities, and wage rates are calculated from the direct labor cost budget and planned direct labor time. Cost Management in Indonesia Mass production factories, such as two- and four-wheeler parts manufacturers common in Indonesia, have multiple manufacturing processes. In such cases, processing costs are calculated for each process, and the method of aggregating these costs into the product is called process costing. In this approach, labor costs and manufacturing overheads are recorded at the end of the month by the accounting department, transferred to inventory assets, and then allocated accordingly. On the other hand, in factories producing custom-made items under individual order production, job order costing is used, where costs are aggregated by order number or project number. In this case, ... 続きを見る

Budgeted Cost in a Cost Management System (Per Item)
A budget means "pre" = beforehand, and "calculation" = to compute, so it involves calculating planned estimates of sales and expenses to predict profit.
In accounting, two critical tasks are financial closing and budgeting. Financial closing is done after a company completes a year of business activities, while budgeting is done before a company begins its yearly operations.
Actual cost refers to the actual product manufacturing cost, standard cost refers to the standard product manufacturing cost, and budgeted cost refers to the budgeted product manufacturing cost.
Product manufacturing costs are grouped into direct material costs, direct labor costs, and manufacturing overhead costs. These can either be calculated deductively using the total average unit price and accumulated allocation expenses or functionally using the three-way method.
In a cost management system, direct material costs are calculated by multiplying the deductively computed total average unit price by input performance. Direct labor costs are allocated directly under the manufacturing department, manufacturing overhead costs are first allocated from indirect departments to direct departments, and the aggregated results are apportioned to products (or work-in-progress).
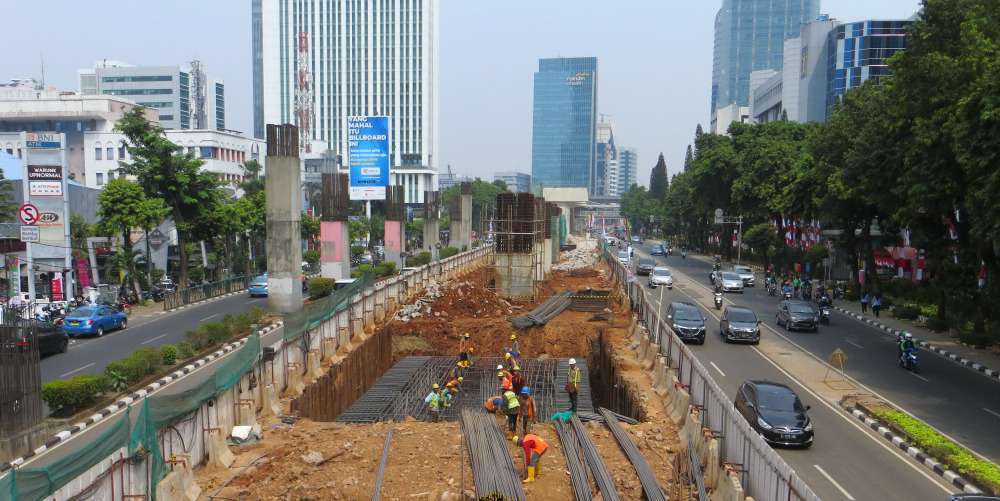
In a cost management system, the variance between standard cost and actual cost is analyzed by breaking down direct material costs into price variance and quantity variance, and direct labor costs into wage rate variance and labor time variance.
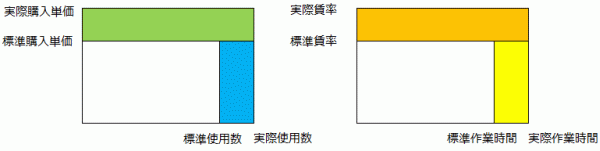
Here, by replacing the master values used in standard costing (standard purchase unit price, wage rate, efficiency, allocation rate) with parameters for budgeted costing, the planned direct material costs and planned direct labor costs can be calculated.
- Standard Purchase Unit Price ⇒ Planned Purchase Unit Price (Purchase Plan Table) ← Master Value
- Standard Usage Quantity ⇒ Planned Input Quantity (Input Plan Table) ← Automatically Calculated
The planned input quantity (Input Plan Table) is automatically calculated from the planned production quantity (Production Plan Table) and BOM.
- Standard Wage Rate (how much per minute) ⇒ Planned Wage Rate (Planned Allocation Cost/Allocation Rate Table)
- Standard Efficiency (how many minutes per unit) ⇒ Planned Efficiency (Planned Direct Labor Time Table)
Budgeted costing is performed by replacing the production performance parameters used in actual costing with parameters for budgeted costing.
- Production Performance ⇒ Planned Production Quantity (Production Plan Table)
Furthermore, by setting the planned sales quantity in the Sales Plan Table and calculating the sales budget, gross profit can be forecasted. In the cost management system, budgeted sales and budgeted product manufacturing costs are calculated, enabling budget vs. actual management with performance (actual costing results).
- Sales Performance ⇒ Planned Sales Quantity (Sales Plan Table)
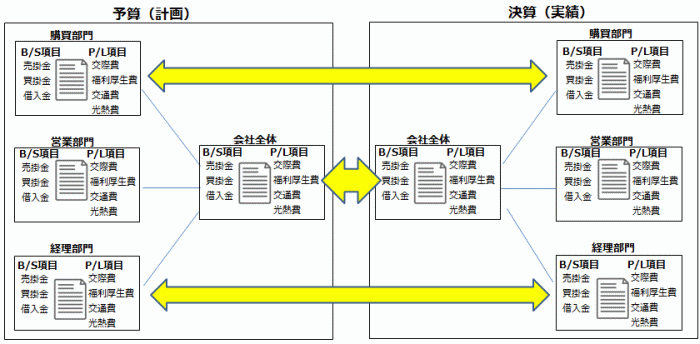
Budget Management in an Accounting System (Per Department and Account)
A major difference between an accounting system and a cost management system in terms of master data is the presence or absence of an item master.
Since an accounting system lacks an item master, aggregating transactions from the general ledger (G/L) by item requires item information. This is where the difference between budget management in an accounting system and a cost management system becomes apparent.
The budgeted cost calculation function in a cost management system computes budgets per item, while the budget management system in an accounting system sets budgets per department via the budget registration screen in terms of profit and loss statement (P/L) and balance sheet (B/S) items. These are automatically aggregated to create the company-wide budget, which is then compared with the finalized P/L and B/S figures after closing in the accounting module for budget vs. actual management.
To perform budget vs. actual management by department, the accounting system’s G/L data P/L and B/S items need to be aggregated by department after closing, requiring proper department settings.
In Japan, labor costs are often the largest expense for companies, but in Indonesia, where labor is cheap, depreciation of machinery might be the biggest cost, or materials might account for the majority of costs.
Project Budget Management
For long-term projects, costs such as materials, outsourcing, and other expenses during the period are transferred to a work-in-progress account or construction-in-progress account and managed as "assets without sales."
Naturally, cost estimates for these are prepared at the project quotation stage. However, in Indonesia, inflation and unpredictable additional costs often cause the initial estimated costs to be exceeded. To protect the original estimated profit, cost items are broadly grouped into materials, outsourcing, and others, balancing the overall figures.
Since estimated costs are roughly finalized at the order registration stage, the project cost management function (Job Costing) registers estimated costs per project. Budget vs. actual management is conducted by issuing purchase orders (P/O) for material purchases or subcontractor services occurring during the project period.



