For items that have beginning inventory but no input performance in the current month, they remain recorded as assets on the B/S and are not expensed as manufacturing costs for the current month. Assuming there is no input-yet-to-be-completed (in-process inventory), the essence of actual cost calculation lies in calculating the manufacturing costs of input items by accumulating them by cost element using the total average unit price and allocating the processing costs of the current process by item. Cost Management in Indonesia Mass production factories, such as two- and four-wheeler parts manufacturers common in Indonesia, have multiple manufacturing processes. In such cases, processing costs are calculated for each process, and the method of aggregating these costs into the product is called process costing. In this approach, labor costs and manufacturing overheads are recorded at the end of the month by the accounting department, transferred to inventory assets, and then allocated accordingly. On the other hand, in factories producing custom-made items under individual order production, job order costing is used, where costs are aggregated by order number or project number. In this case, ... 続きを見る

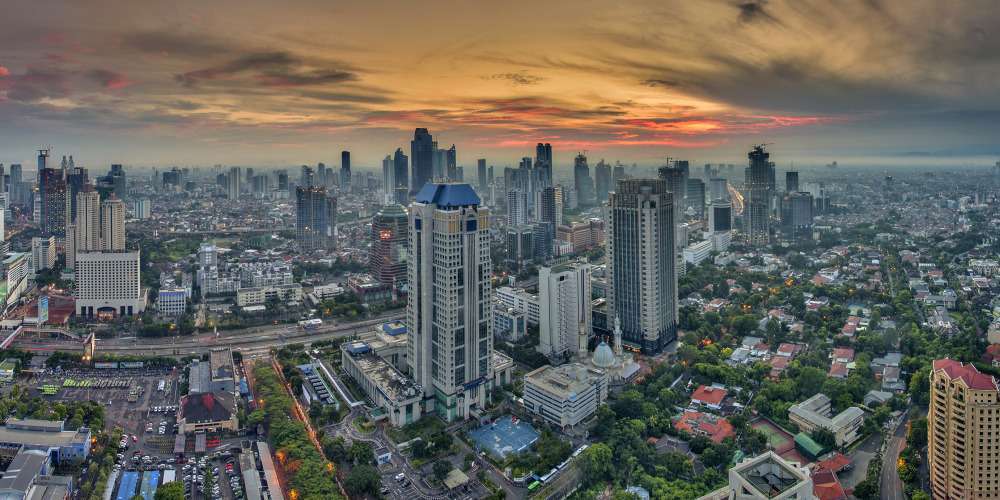
Manufacturing Cost Calculation Using the Total Average Method
Manufacturing costs are calculated using the periodic inventory method as "beginning WIP + monthly manufacturing expenses - ending WIP." Transferring the manufacturing costs of the previous process to the current month's manufacturing expenses of the current process and calculating product costs in a multi-level manner using the periodic inventory method is called the rolling costing method.
On the other hand, with the total average method, manufacturing costs are calculated as "monthly total average valuation of input items + expenses incurred in the current process." The total average unit price is calculated sequentially from materials to products, and the costs of each process are accumulated using "(total average unit price × actual input quantity) + processing costs incurred in the current process," which is referred to as the buildup method.
Since both the rolling costing method and the buildup method ultimately yield the same results, it is generally thought that the two terms are used synonymously.
- Total average unit price = (beginning inventory amount + monthly manufacturing costs) / (beginning inventory quantity + monthly production quantity)
A characteristic of the total average method is that it allows the calculation of issuance costs using the total average unit price, taking into account beginning inventory information. The total average unit price of the items produced in the current process is applied as the unit price for the actual input in the next process.
- Actual input quantity × total average unit price
- Direct labor costs (costs incurred in the current process)
- Manufacturing overhead costs (costs incurred in the current process)
This total becomes the manufacturing costs for the current month. The total average unit price is calculated by factoring in the beginning inventory, and it is applied as the unit price for the actual input in the next process, ultimately becoming the product manufacturing cost in the final process.
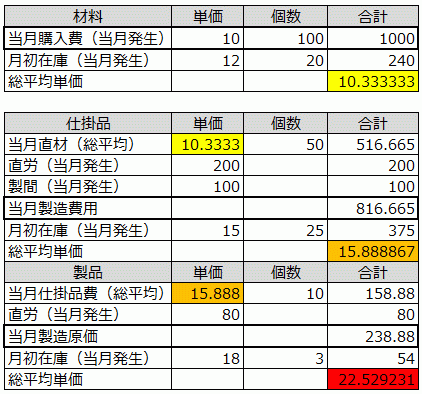
Concept of the Cumulative Method (Buildup Method)
In a production management system, receipt and issuance quantities are managed according to the ledger linkage chart, and the manufacturing costs (costs of items manufactured in the current month) are calculated in the cost management system. First, the direct material costs input into the initial process are calculated using the total average method.
- Direct material costs = Total average unit price of input materials × input quantity
The WIP manufacturing cost, which is the direct material costs plus processing costs, is considered the incurred cost of the input items for the next process, and the WIP manufacturing cost of the next process is similarly calculated using the total average method.
- Cost of input WIP = Total average unit price of input WIP × input quantity
This method of repeatedly adding the processing costs to the cost of the input WIP as input items in subsequent processes is called the cumulative method (Cumulative Method = Rolling Costing).
The material costs based on the issuance quantity, which is part of the issued materials, become the incurred costs based on the input quantity to WIP. The WIP costs based on the production quantity, which is part of the produced WIP, become the incurred costs based on the input quantity to the product. The cost of sales based on the shipment quantity, which is part of the shipped products, becomes the final cost.
Typically, since materials and WIP become inventory or are used as common materials for multiple products, the incurred costs based on the production quantity of the current process are generally greater than the incurred costs based on the input quantity of the next process.
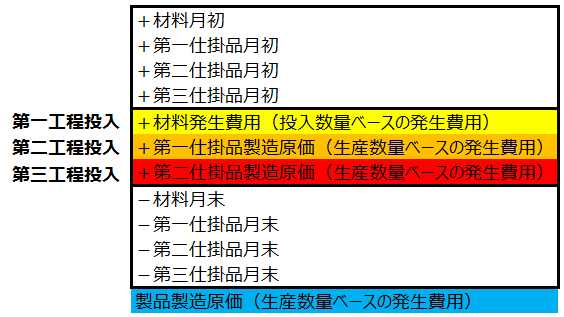
Non-Cumulative Method
In cases where materials or WIP are not common materials, the monthly incurred material costs or the incurred costs based on the production quantity of the current process become 100% of the incurred costs based on the input quantity of the next process. For products, 100% of the incurred costs based on the production quantity (manufacturing costs) become the incurred costs based on the receipt quantity of the product.
In contrast to the cumulative method, where the incurred costs of the current process are accumulated as the input costs of the next process according to the ledger linkage chart, the non-cumulative method (Non-Cumulative Method) treats the first to third processes as a single process and calculates the product manufacturing costs all at once.
In other words, the cumulative method considers the product as an accumulation of cost element codes by process, while the non-cumulative method aggregates the costs incurred in each process directly into the cost element codes of the product itself.
Relationship Between Manufacturing Costs and Total Average Unit Price
The certification scandal of a major automaker has been a hot topic recently. If shipments are halted for several days, the production volume for that month drops significantly. When production volume decreases, the proportion of fixed costs such as depreciation and labor costs per product unit increases, resulting in higher manufacturing costs per product unit.
Since monthly fixed costs remain constant while production quantities are adjusted to market changes, calculating manufacturing costs based solely on actual production quantities leads to short-sighted cost management. Therefore, a standardized cost leveled throughout the year is determined before preparing the budget for the next period, forming the basis for sales and procurement plans.
Cost variance represents how much the monthly manufacturing costs deviate from this unchanging annual standard cost. Cost variance analysis breaks down these variances into factors such as material purchase prices, purchase quantities, and operating hours.
Thus, cost variance indicates the extent to which the current month’s manufacturing costs deviate from the standard cost, which serves as the baseline. Naturally, the inventory accumulated at the beginning of the month bears no responsibility for this cost variance, but at the time of shipment, both the inventory and the current month’s production are lumped together and evaluated at the total average, ultimately sharing joint responsibility as the unit cost of sales.
The manufacturing cost unit price refers to the unit price of the current month’s production, while the total average unit price is the overall unit price combining the beginning inventory and the current month’s production. The total average unit price of the product is the unit cost of sales.
This is often confusing, but when it is said that “manufacturing costs are calculated using the total average unit price,” it does not mean “total average unit price of the product × production quantity.”
The total average unit price of the product is calculated based on “beginning product inventory + monthly product manufacturing costs” and is determined after the manufacturing costs, which is why.
Thus, the total average unit price available at the time of calculating manufacturing costs is limited to the total average unit price of the input items, as the total average unit price is calculated from downstream to upstream.
The total average unit price is calculated by cost element and reflected in the current period’s manufacturing costs of the input items for the next process by cost element.
- Direct material total average unit price = (beginning direct material + monthly direct material) / (beginning quantity + monthly quantity)
- Direct labor total average unit price = (beginning direct labor + monthly direct labor) / (beginning quantity + monthly quantity)
- Manufacturing overhead total average unit price = (monthly overhead + monthly overhead) / (beginning quantity + monthly quantity)
These total average unit prices by cost element are accumulated as they move upstream, but cost elements that incur no costs in the current process remain equal to the accumulated costs of the previous process and are not recorded as incurred costs by cost element. The monthly manufacturing costs are the evaluation of the incurred costs of input items in each process using the total average unit price by cost element.
Accumulation Calculation of Total Average Unit Price by Cost Element
If the accumulation calculation of the total average unit price by cost element can be performed, the monthly manufacturing costs by cost element can be automatically calculated by multiplying it by the usage quantity.
The total average unit price is calculated only after the monthly manufacturing costs and beginning inventory amount are available, and it serves as the basis for the valuation amount of the actual input in the next process. The monthly manufacturing costs are the sum of the valuation amount of the actual input based on the total average unit price and the processing costs of the current process (via allocation). Repeating this process from upstream (materials) to downstream (products) yields the manufacturing costs and total average unit price of the final product.
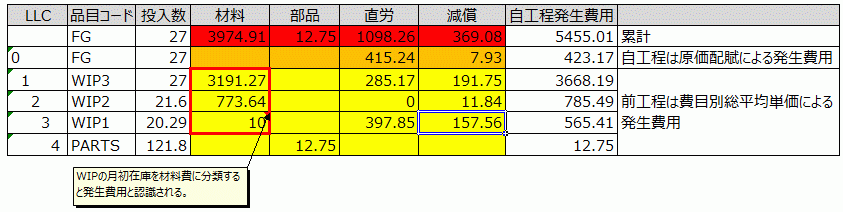
The total average unit price is accumulated by cost element from upstream to downstream, and the difference from the accumulated amount up to the previous process becomes the total average unit price of the costs incurred in the current process.
Process Costing is Suited for Anticipatory Production (Mass Continuous Production = Mass Production)
Manufacturing costs calculated using the periodic inventory method as "beginning WIP + monthly manufacturing expenses - ending WIP" are calculated in the total average method as "total average valuation of input items + expenses incurred in the current process." Therefore, it is necessary to calculate the total average unit price sequentially from materials to products.
Factories adopting process costing typically have multiple manufacturing processes, with process costs calculated for each process. There are two methods to aggregate these into product costs: the cumulative method and the non-cumulative method.
The cumulative method (Cumulative Method) transfers the manufacturing costs of the previous process (beginning + monthly expenses - ending) as the input costs of the current process and calculates product costs in a multi-level manner using the periodic inventory method, known as rolling costing, which closely resembles the ledger linkage chart.
- 1st Process: Beginning WIP 1 + monthly materials + monthly processing 1 - ending WIP 1 = monthly WIP 1 manufacturing costs
- 2nd Process: Beginning WIP 2 + monthly WIP 1 manufacturing costs + monthly processing 2 - ending WIP 2 = monthly product manufacturing costs
"Rolling Costing" is both "accumulation calculation" and "rolling costing," a "cumulative method" that sequentially accumulates the processing costs of each process according to the ledger linkage chart, starting from material costs.
The non-cumulative method (Non-Cumulative Method) calculates the costs of each process at a single level without including the costs of the previous process and directly sums them to determine the product costs.
- (Costs of the 1st process in the product)
Beginning WIP 1 + beginning WIP (1st portion of the 2nd) + monthly processing 1 - ending WIP 1 - ending WIP (1st portion of the 2nd)
- (Costs of the 2nd process in the product)
Beginning WIP (2nd portion of the 2nd) + monthly processing 2 - ending WIP (2nd portion of the 2nd)
- 1st process costs + 2nd process costs = monthly product manufacturing costs
Receipt and Issuance Performance Data for the Total Average Method
The performance data generated in the production management system for the process of purchasing materials, supplying processed WIP to an subcontractor free of charge, and shipping the subcontractor-processed products are shown in the figure below.
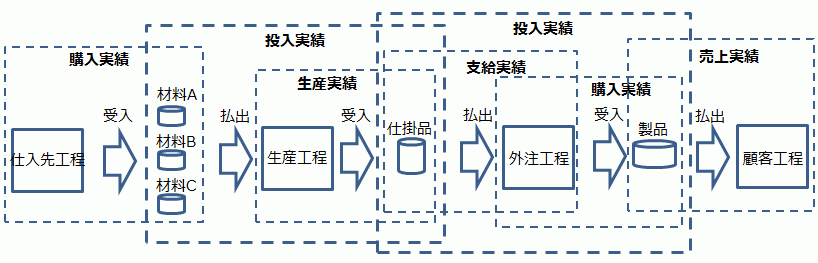
- Issuance performance ⇒ For transfer to other accounts
Spoilage due to defects or inventory shrinkage is deducted from the cost of sales. The WIP unit price is evaluated by accumulating "total average unit price + processing costs" for the current month. - Input performance ⇒ For direct material cost calculation
Incurred costs based on input, indicating how many child items were input to the parent. - Production performance ⇒ For direct material cost calculation
Incurred costs based on production, indicating how many parent items were produced. - Supply performance ⇒ For direct material cost calculation
How many items were supplied to the subcontractor. - Purchase/subcontracting performance ⇒ For direct material costs and subcontracting processing cost calculation
How much the purchase costs were for materials and how much the subcontracting processing costs were for products. - Sales performance ⇒ For cost of sales calculation
Calculates gross profit.



